What is hypothesis?
Question to resolve
Happy day, amazing people!!!
Hypothesis is a proposition or an assumption or a well-known fact.
Ok guys, let me put that in simple terms.
Earlier people were thinking that planet earth was flat but after some researches it was found to be round, to be more specific it’s a sphere.
From the above example, we could see that how a proposition or an assumption was disproved. Likewise, in any research there will be an existing truth or an assumed truth which a researcher wants to disprove.
Hence, the research will always start with a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
Null hypothesis is the one which we were talking about existing truth or assumed truth which a researcher wants to disprove.
H0: Earth is flat
And on the other hand, alternate hypothesis is the one which a researcher wants to prove.
Ha: Earth is not flat
Procedure in testing hypothesis
Formulation of hypothesis
First step for a researcher is to come up with null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.
Let’s say Timothy wants do a research.
Early researches or existing truth is that a person can blink his eyes 15 times in a minute on an average. Timothy disbelieves this and wants to disprove it. So, his null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis would be
H0: A person blinks his eyes 15 times in a minute on an average
H0: µ = 15
Ha: A person does not blink his eyes 15 times in a minute on an average
Ha: µ ≠ 15
This is a two tailed test, which means that there is no direction to the research. It just tells us whether humans blink their eyes 15 times or not.
If Timothy wants to prove that a human blink his eyes more than 15 times in a minute on an average, then his alternate hypothesis would be (Right tailed test)
Ha: A person blinks his eyes more than 15 times in a minute on an average
Ha: µ > 15
On the flip side, if Timothy wants to prove a human blinks less than 15 times in a minute on an average, then his alternate hypothesis would be (Left tailed test)
Ha: A person blinks his eyes less than 15 times in a minute on an average
Ha: µ < 15
Selecting the significance level
Next step is to set a significance level. We have all heard that it is usually 0.05 or 0.01 but it depends upon the research bring carried out. These level shows the rejection region on the normal distribution curve, which means that when a test statistic value falls in these regions null hypothesis is rejected.
For two tailed test, rejection region is on the both the sides of the curve. (i.e., At 0.05 significance level, rejection region of 0.025 is present on both the sides of the curve) as shown in the diagram.
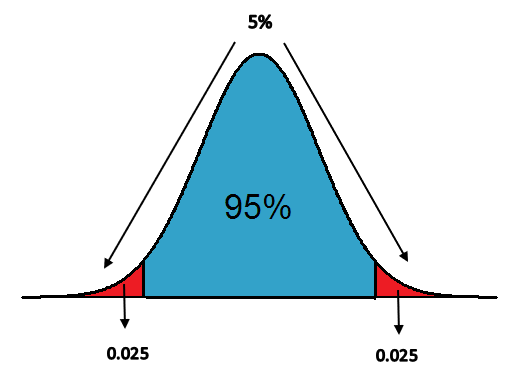
And for one tailed test, rejection region is on the one side only. For right tailed test, rejection region is on the right side of the curve and for left tailed test, rejection region is on the left side of the curve. Timothy is taking 0.05 as his significance level for his research.
Deciding on the test statistic
Depending upon the research, Timothy has to choose which of the tests to be used to get the value. Some of the most commonly used tests are Z-test, T-test, F-test, Chi-square test, ANOVA etc.
For his research Timothy is choosing T-test
Setting the critical region
Critical region is a region which separates rejection region from acceptance region. Critical region is found out by using the respective table. Here in this case Timothy is using T-test table.
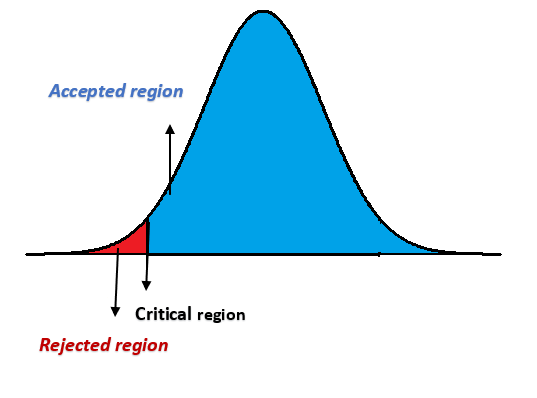
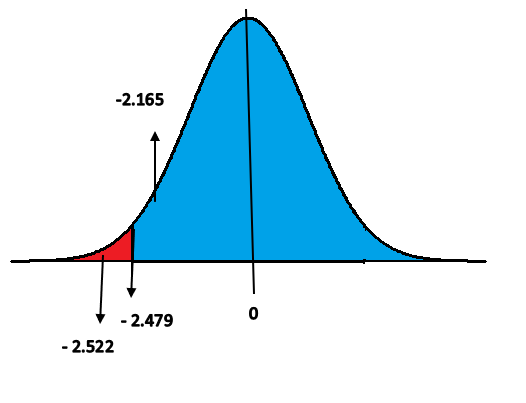
Let’s say Timothy wants to prove that a person blinks less than 15 times in a minute on an average (Ha: µ< 15). He knew that this is a one tailed test and for example let’s say with the help of degree of freedom he found out the critical value to be – 2.479. It is negative because it is a left tailed test.
Computing the value of test statistic
Timothy used T-test formula to compute the t value. This value tells us whether we should reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
We know the formula is
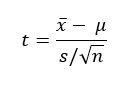
Drawing the conclusion
Final step is to draw conclusion from the values.
Let’s imagine T value to be – 2.165, this value is not beyond – 2.479 and it falls on the acceptance region. Hence, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
So, the conclusion would be that there is no enough evidence to prove that a person blinks less than 15 times in a minute on an average. Hence, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
On the other hand, if the T value is – 2.522 which is beyond – 2.479 and also falls in the rejection region. Then we should reject the null hypothesis.
Here the conclusion would be that there is enough evidence to prove that a person blinks less than 15 times in a minute on an average. Hence, we reject the null hypothesis.
We hope you guys have understood about hypothesis and testing of hypothesis.
Ok then, before signing off
Love what you do, do what you love…. Bye
From,
Simply grasp