By passing the funnel pathway
Happy day, amazing people!!!
Let’s understand sampling design through a short anecdote.
Nila, a post graduate student was running down the corridor to attend her classes. She was in such a rush because the professor has asked all the students to be a little early for that day’s class.
While running she show a juice carton laying on the floor, immediately she stopped, picked it up and throw it in the trash can.
After reaching the class she was relieved to know that her professor has not yet come. She was standing on the entrance and taking heavy breaths. Her friend called her by her nickname, “Eco freak” to come and sit beside them. As they were expecting their professor any time soon.
The Professor entered the room and started telling bout the final year research project which they have to submit.
Nila thought through and wanted to incorporate here interest for nature preservation in her research project.
She lives in a place called Bamias. It is surrounded by beautiful landscape, natural flora, and fauna. Which she loves and adores. Due to recent industrialization, industries started polluting Bamias’s soil, air, and water bodies.
Nila understands the importance of industrialization for economic growth but also, worries about her beloved Bamias. So, she decided to conduct research on CSR activities done by textile industry of Bamias towards environment. She chose textile because it was predominant in her place.
So here comes the funnel path which Nila has to pass through.
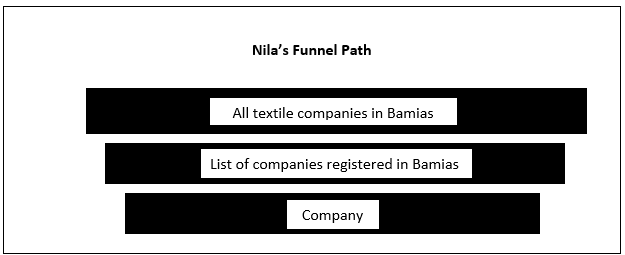
Stage 1: Universe
All items in any field of inquiry are called ‘universe or population.’ The universe can be finite (i.e., no. of items is certain) or infinite (i.e., no. of items is uncertain).

Stage 2: Sample Frame
Sample frame also knows as source list contains the names of all items of a universe.

Stage 3: Sampling Unit
Sampling unit refers to the singular value within a sample database. It can be geographical unit (city, state, etc.), construction unit (house, flat, etc.), social unit (family, club, school, etc.) or just individual.
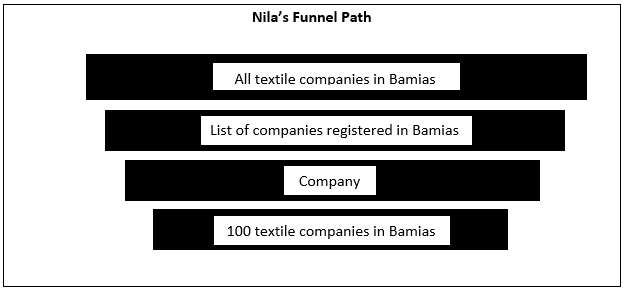
Stage 4: Size of Sampling
Size of sample refers to the no. of items to be selected from the universe to constitute a sample. It depends upon various factors including confidence level (i.e., it is the level at which even if the research was to be repeated, we would get the same results. Usually it is 90 % and 95%), parameter of interest (like average, percentage etc.), cost, size, sand variability of population.
Stage 5: Sampling Procedure
Sampling procedure is the decision about the technique to be used in selecting the items for the sample. There are two major types, probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Probability Sampling – Every element in the population has an equal probability of getting into the sample
Non-Probability Sampling – Not all elements of the population have an equal chance of participating in the study
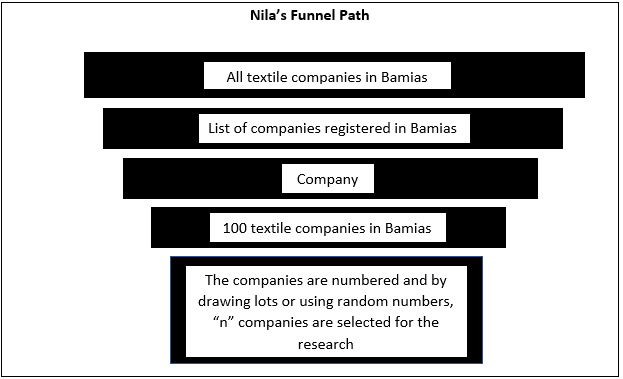
Voila, this is how sampling design is generally done.
Now by keeping the above example lets look at the different sampling procedure.
Sampling Procedures:
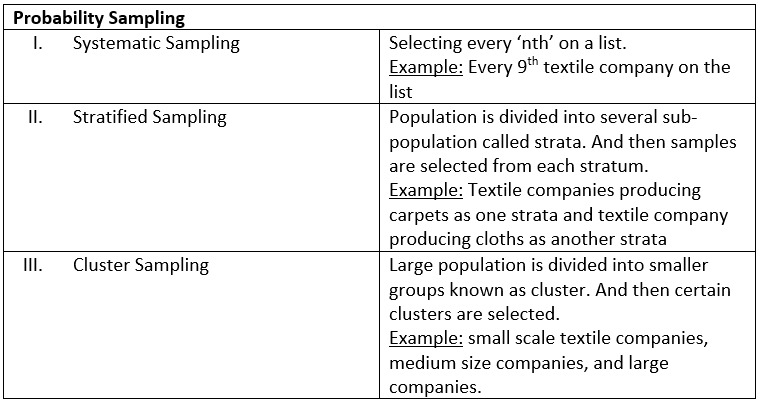
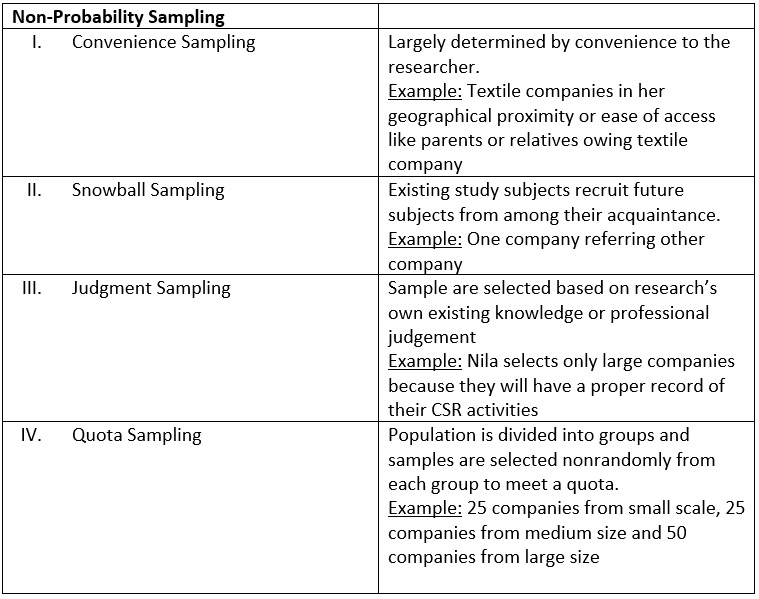
We hope you guys have understood about how to do sampling design for research.
Ok then, before signing off
Love what you do, do what you love…. Bye
From,
Simply grasp